All DSP releases prior to DSP 1.4.0 use Gravity, a Kubernetes orchestrator, which has been announced end-of-life. We have replaced Gravity with an alternative component in DSP 1.4.0. Therefore, we will no longer provide support for versions of DSP prior to DSP 1.4.0 after July 1, 2023. We advise all of our customers to upgrade to DSP 1.4.0 in order to continue to receive full product support from Splunk.
Filtering and routing data in the
The can filter data so that only records that match a specified condition can pass downstream to other functions in your pipeline. For example, you can configure the Where function to look for a specific event code from Windows event logs, and only allow records with that event code to be sent to the end of the pipeline.
You can also route data to different destinations depending on whether the data meets certain filter criteria. For example, you can branch the pipeline and configure multiple Where functions so that all data from one data source is sent to a Splunk index, all data from a second data source is sent to a different Splunk index, and all data from a third data source is sent to a third-party destination like Apache Kafka. See the Create a pipeline that routes data to different Splunk indexes section on this page for an end-to-end example of how to build a pipeline that routes data depending on filter criteria.
Filter records using the Where function
Add a Where function to your pipeline to only allow records that match a specified condition to pass downstream to other functions in your pipeline.
- From the Canvas view of your pipeline, click on the + icon and add the Where function to your pipeline.
- In the Where function, provide a predicate expression. For examples of predicate expressions, see the Where function, the Predicate expressions section on this page, or the predicates topic in the SPL2 Search Manual.
- With the Where function highlighted, click Start Preview
 to verify that the expression is working as expected.
to verify that the expression is working as expected.
Predicate expressions
The following table lists some common expressions that you can use in the Where function. The Where function accepts a predicate, which is an expression that returns a boolean value (true or false). See Predicates for more information on predicates.
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| kind="metric" | If the kind field is equal to metric, the record passes downstream. If not, the record doesn't get passed through the pipeline.
|
| source_type LIKE "CISCO%" | If the source_type field contains the string, "cisco", the record passes downstream. If not, the record doesn't get passed further through the pipeline. |
| ttms > 5000 | Here, ttms is a custom top-level field that contains latency information. If the record has a ttms value of over 5 seconds, the record is passed downstream. If not, the record doesn't get passed through the pipeline.
|
| NOT (timestamp IS NULL) | If the timestamp field is not null, the record passes downstream. If timestamp is null, the record doesn't get passed through the pipeline. |
| logGroup LIKE "/c/windows/%" OR logGroup LIKE "/aws/directoryservice/%" | Here, logGroup is a custom top-level field containing a specific path. If the logGroup field contains "/c/windows/%" or "/aws/directoryservice/%", the record passes downstream. If not, the record doesn't get passed further through the pipeline.
|
| map_get(attributes, "spl_fwd_type")="uf" | Here, we are ingesting data from a Splunk universal forwarder, which outputs a map of key-value pairs in the attributes field. One of these key-value pairs is spl_fwd_type: "uf". In this example, the map_get scalar function is looking through the attributes map for the spl_fwd_type: "uf" key-value pair. If it finds this key-value pair, then the record passes downstream. If not, the record doesn't get passed further through the pipeline.
|
Create a pipeline that routes data to different Splunk indexes
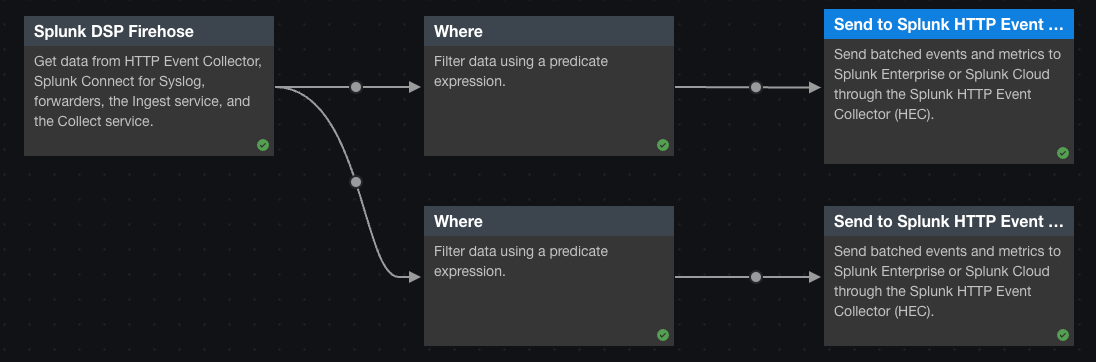
In this example, we create a pipeline that does the following:
- Ingests data from the Splunk DSP Firehose. In this case, the Splunk DSP Firehose is receiving data from a combination of sources including a Splunk Connect for Syslog (SC4S) instance.
- Sends syslog data to a Splunk index called
syslog. - Sends all other data to the Splunk index specified in the
attributesfield of the record, or to the default index calledmainif theattributesfield does not specify an index.
Prerequisites
- A SC4S instance that is configured to send data to the . See Configure SC4S to send syslog data to the in the Connect to Data Sources and Destinations with the manual.
- A connection to your Splunk instance. See Create a connection to a Splunk index in the Connect to Data Sources and Destinations with the manual.
Steps
- From the Pipelines page, select the Splunk DSP Firehose data source.
- Configure the pipeline to send syslog records to a Splunk index named
syslog. To achieve this, filter for records that have thesource_typefield set tosyslog, so that only records that match that criteria can continue downstream to the sink function.- Click the
 icon beside the Splunk DSP Firehose function and select the Where function.
icon beside the Splunk DSP Firehose function and select the Where function. - On the View Configurations tab, in the predicate field, enter the following expression:
source_type="syslog"
- Click the
 icon beside the Where function and select the Send to a Splunk Index with Batching sink function.
icon beside the Where function and select the Send to a Splunk Index with Batching sink function. - On the View Configurations tab, set connection_id to the connection for your destination Splunk instance.
- In the index field, enter "" (two quotation marks).
- In the default_index field, enter "syslog" (including the quotation marks).
- Click the
- Configure the pipeline to send all other records to the Splunk index specified in the
attributesfield, or to themainindex if theattributesfield doesn't specify an index. To achieve this, create a branch in the pipeline that filters for records that have asource_typeother thansyslog, so that only records that match that criteria can continue downstream to the second sink function.- Click the
 icon beside the Splunk DSP Firehose function and select the Where function.
icon beside the Splunk DSP Firehose function and select the Where function. - On the View Configurations tab, in the predicate field, enter the following expression:
source_type!="syslog"
- Click the + icon beside the Where function and select the Send to a Splunk Index with Batching sink function.
- On the View Configurations tab, set connection_id to the connection for your destination Splunk instance.
- In the index field, enter the following expression:
cast(map_get(attributes, "index"), "string")
- In the default_index field, enter "main" (including the quotation marks).
- Click the
- Validate your pipeline to confirm that all of the functions are configured correctly. Click the More Options
 button located beside the Activate Pipeline button, and then select Validate.
button located beside the Activate Pipeline button, and then select Validate. - Click Save, enter a name for your pipeline, and then click Save again.
- (Optional) Click Activate to activate your pipeline. If it's the first time activating your pipeline, do not enable any of the optional Activate settings.
You now have a pipeline that receives data from the Splunk DSP Firehose, sends any data that was ingested from a syslog server to the syslog index in your Splunk instance, and sends all other data to either the index specified in the attributes field or the default main index.
The following is the complete SPL2 statement for this pipeline:
$statement_2 = | from splunk_firehose();
| from $statement_2 | where source_type!="syslog" | into into_splunk_enterprise_indexes("2f1ce641-baeb-4695-82cc-8f16ae64eb71", cast(map_get(attributes, "index"), "string"), "main");
| from $statement_2 | where source_type="syslog" | into into_splunk_enterprise_indexes("2f1ce641-baeb-4695-82cc-8f16ae64eb71", "", "syslog");
See also
| Remove unwanted fields from your data | Adding and updating fields in the |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Data Stream Processor: 1.3.0, 1.3.1, 1.4.0, 1.4.1, 1.4.2, 1.4.3, 1.4.4, 1.4.5, 1.4.6
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!