About risk-based alerting in Splunk Enterprise Security
Splunk Enterprise Security uses risk-based alerting (RBA) to accelerate and simplify the process of detecting risk in your security environment. The Risk Analysis framework integrates directly with content management in Splunk Enterprise Security to provide context and enrich raw data. Using a risk based lens helps security teams to pivot from a traditionally reactive to a proactive approach towards threat detection.
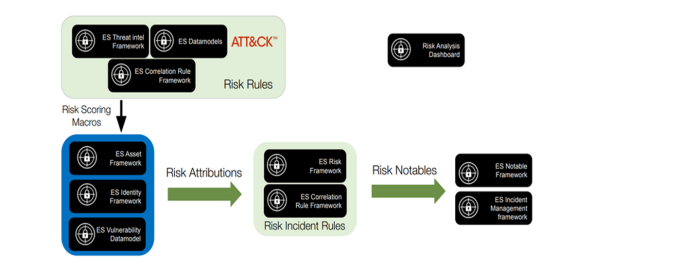
The following illustration provides an overview of how RBA works in Splunk Enterprise Security:
As a security analyst or threat detection engineer, who is responsible for identifying threat and prioritizing risk incidents in your security environment, you can use risk incident rules to generate risk notables instead of using the Splunk Search Processing Language (SPL) to drill down on massive volumes of alerts or raw data. With RBA, you can create high fidelity notables based on risk and thus, increase true positive rates. You can also frame how risk notables relate to specific assets or identities and develop security stories based on user behaviors to proactively identify threats within an enterprise. This can help you to focus on higher impact tasks such as threat hunting and adversary simulation, instead of manually triaging notables.
Use RBA to identify the most difficult-to-detect security use cases:
- Insider threats
- Compromised user accounts
- Compromised systems
- Recurring infections
- Suspicious use of credentials
- Lateral movement
- Living off-the-land cyber-attacks.
This manual helps you to set up your security operations center (SOC) with RBA using Splunk Enterprise Security and provides best practice guidance on assigning risk scores, creating risk factors, reviewing risk notables, and modifying risk-incident rules to manage risk in your security environment.
Begin your RBA journey
You can also use the Splunk App for Fraud Analytics to detect fraud. This app uses the RBA framework to provide high fidelity and actionable fraud alerts for account takeovers and new account fraud. You can also use this app to get started with RBA using some default searches and dashboards even if you do not have prior knowledge of SPL.
Download and install the Splunk App for Fraud Analytics in your Splunk Platform environment from Splunkbase. For more information on the app, see Splunk App for Fraud Analytics User Guide.
Additionally, you can contact your Splunk Sales representative to deploy this app along with your existing Splunk Enterprise Security deployment. With this app, you can display fraud related alerts and drill down on fraud analysis dashboards in Splunk Enterprise Security.
You do not need to download the app to use RBA in Splunk Enterprise Security.
Advantages of using risk-based alerting in Splunk Enterprise Security
Using RBA to analyze risk in your security environment offers the following advantages:
- Proactively address threats and identify security gaps with leading cybersecurity frameworks
Apply insights from cybersecurity frameworks such as MITRE ATT&CK, CIS 20, and NIST Controls to create visualizations that highlight the tactics and techniques observed in risk events. You can use these visualizations to quickly build situational awareness around a given user or system in the context of the ATT&CK matrix and view the associated documentation on a given technique. With this additional context, you can proactively detect threats such as adversary simulation. With your preferred framework, you can also quantify security gaps and identify the MITRE tactics covered to plan your response without using SPL. - Identify relationships between threat actors using visualizations
Visualizations such as Threat Topology and Risk Event Timeline enables analysts to quickly visualize relationships between malicious threat actors and their users and systems when working with risk notables. Analysts can discover the scope of a security incident immediately and quickly pivot between affected assets and identities in the investigation. - Detect complex threats by expanding security coverage
Surface attacks by building a comprehensive collection of attributes. You can build investigations that span over longer periods of time and prevent malicious tactics that infiltrate the SOC through low-level attacks. For example, you can configure alerts when an entity's behavior spans three or more MITRE ATT&CK tactics over a two-week period, expanding your security coverage. - Streamline investigations and remediation
Reduce the triage time for security incidents by providing context to the investigative process and reducing alert volume, which helps analysts to focus on other high-value activities within the SOC.
See also
For more information about how best to use RBA in your security environment, see the product documentation.
How RBA works in Splunk Enterprise Security
Managing risk using risk based alerting in Splunk Enterprise Security
| How risk-based alerting works in Splunk Enterprise Security |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise Security: 7.3.2, 7.3.3
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!