Use Function Calling LLM-RAG
You can use Function Calling-based LLM through a set of dashboards. The following processes are covered:
All the dashboards are powered by the fit command. The dashboards showcase Function Calling LLM-RAG functionalities. You are not limited to the options provided on the dashboards. You can tune the parameters on each dashboard, or embed a scheduled search that runs automatically.
The results you see when using Function Calling LLM-RAG depend on your customizations. The examples provided here do not necessarily reflect the custom tools you might use in your own use cases.
Configure LLM service
Make sure that you have enabled the LLM service(s) of your choice on the Setup LLM-RAG (optional) page prior to starting the container. If you have not, finish the configuration and restart the container.
For downloading local LLMs, refer to the relevant sections in Use Standalone LLM.
Implement the Function tool
Complete the following steps:
- Select the JupyterLab link listed on the container management page. The default is https://<docker host ip>:8888.
- Navigate to notebooks and open the notebook named llm_rag_function_calling.ipynb.
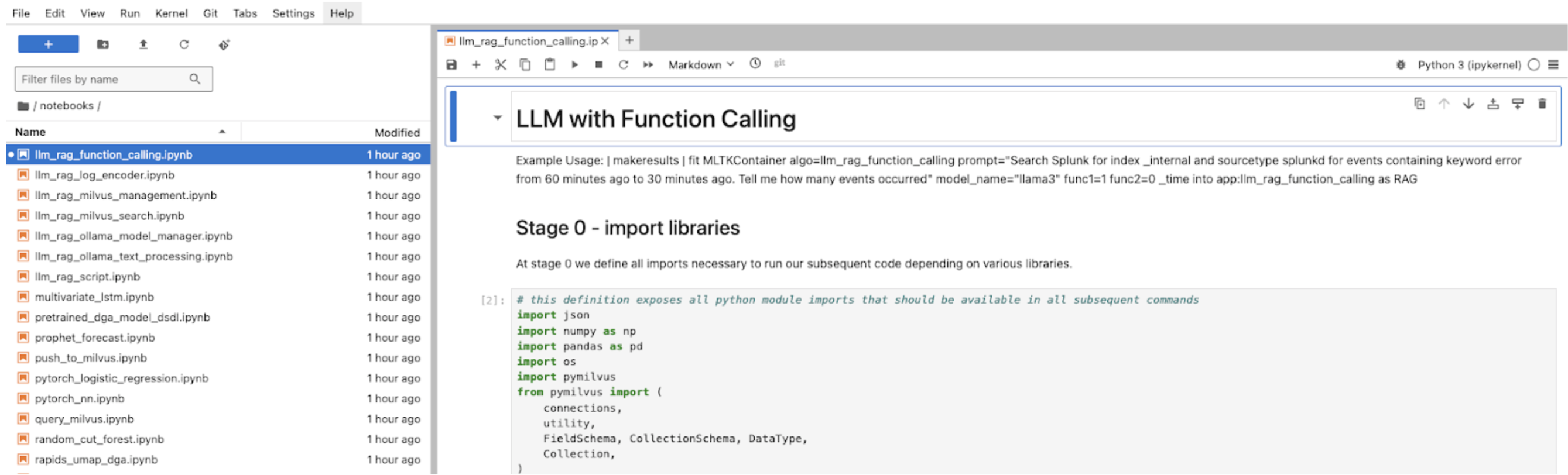
- In the cell Stage 0 - import libraries you can find the following pre-defined Python functions:
- Search splunk
- List indexes
- Get index info
- List saved searches
- List users
- Get indexes and sourcetypes
- Splunk health check
search_splunk_tool = FunctionTool.from_defaults(fn=search_splunk) list_indexes_tool = FunctionTool.from_defaults(fn=list_indexes) get_index_info_tool = FunctionTool.from_defaults(fn=get_index_info) list_saved_searches_tool = FunctionTool.from_defaults(fn=list_saved_searches) list_users_tool = FunctionTool.from_defaults(fn=list_users) get_indexes_and_sourcetypes_tool = FunctionTool.from_defaults(fn=get_indexes_and_sourcetypes) health_check_tool = FunctionTool.from_defaults(fn=health_check)
- You can add comments to each function explaining the format and meaning of each input variable. This allows the LLM to set each parameter when it calls the function. To give the LLM access to a certain function tool use the cell Stage 4 - apply the model.
- In the cell, a list called
tool_listis created and the function tool objects initialized in Stage 0 are appended to the list. By appending the function tool to the list, the LLM can access to the function tool and runs the tool when necessary to gain additional contextual information.
Implement your own Function Tool
You can register your own function tool by completing the following steps:
- Write a simple Python function in the cell Stage 0 - import libraries:
def MyFunction(a: int, b: int): return a + b - Wrap the Python function as a Function Tool in the cell Stage 0 - import libraries:
MyFunctionTool = FunctionTool.from_defaults(fn=MyFunction)
- Register the function to the tool list in the cell Stage 4 - apply the model:
tool_list = [..., MyFunctionTool, ...] worker = ReActAgentWorker.from_tools(tool_list, llm=llm)
The input parameters of the fit command are Booleans that indicate if you are using Function 1 (func=1) or Function 2 (func2=0). If you implement your own function tool but want to keep the default fit command syntax, you must substitute the default tools with your own function tools in the positions of func1 and func2 when you wrap the functions in the cells.
Alternatively, you can define new parameters of the fit command or hardcode the tool list.
Use Function Calling LLM-RAG
Complete the following steps:
- In DSDL, navigate to Assistants, then LLM-RAG, then Querying LLM, and then select LLM with Function Calling.
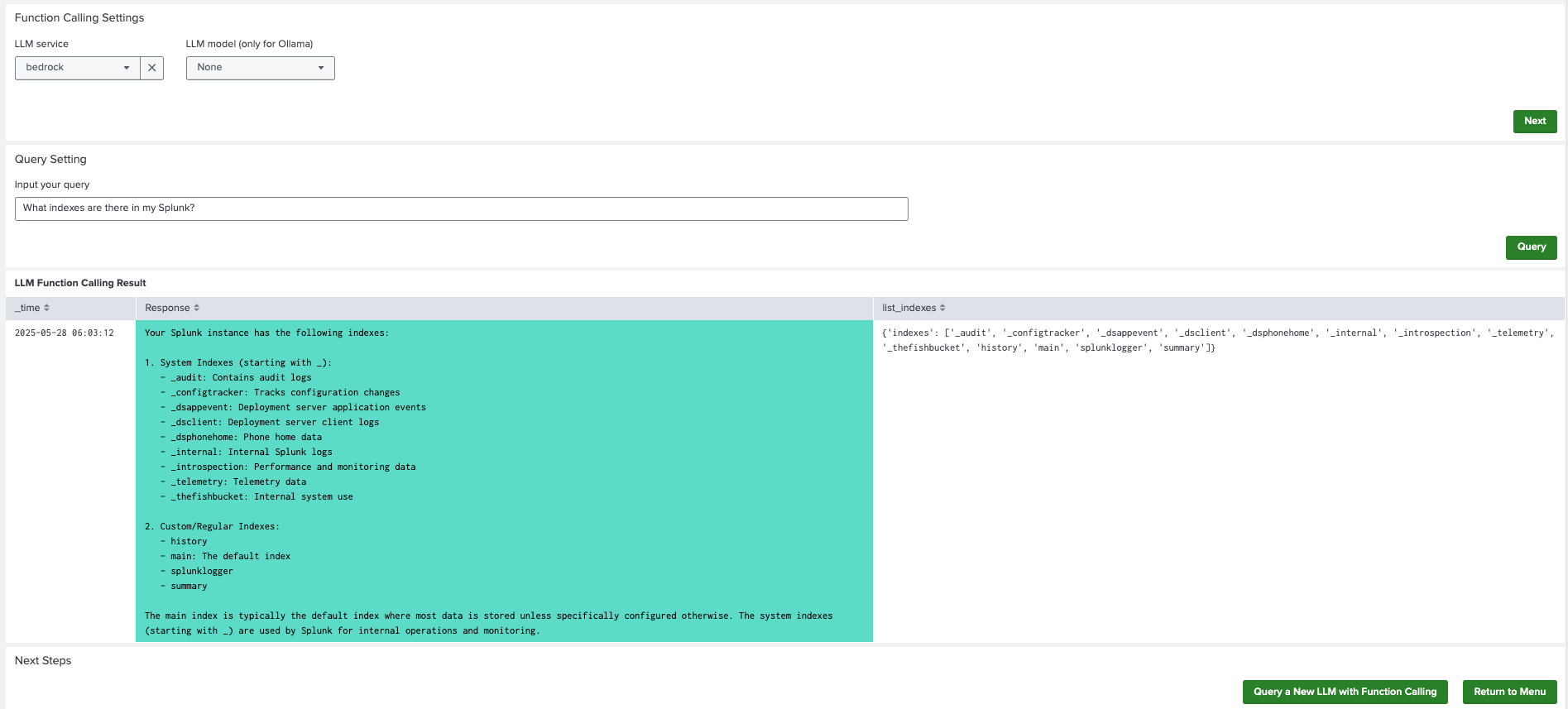
- On the LLM-RAG settings panel, select the LLM service you want to use.
- Select Next to submit the settings.
- An Input your query field becomes available. Input your query and select Query. The final output for the LLM and the result for each function tool appears.
| Use Document-based LLM-RAG | Encode data into a vector database |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® App for Data Science and Deep Learning: 5.2.1
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!