Batch Events to optimize throughput to Splunk Enterprise indexes in DSP
You can transmit multiple events in one request in the Data Stream Processor (DSP) with batching. Batching events, as opposed to packaging each event individually, can increase throughput by reducing the net amount of data being transmitted. To batch events, use the Batch Events streaming function after doing any desired data transformations in your pipeline.
Routing batched data to different indexes
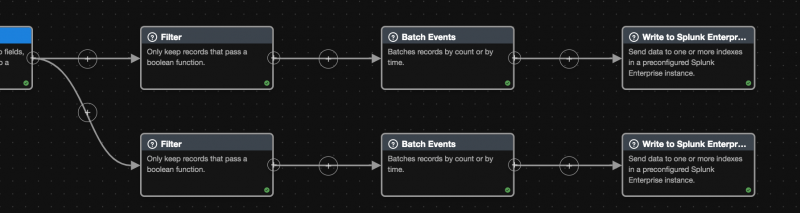
Right now, you can only designate an index to send your data to using the Write to Splunk Enterprise or Write to Index sink functions. Because batching applies any function arguments across the entire batched payload, the index you provide in your Write to Splunk Enterprise or Write to Index functions gets assigned to the entire payload. Therefore, if you want to send batched data to specific indexes, you must make one branch per index that you want to send data to.
Example
Prerequisites
- A data pipeline with a source function.
- A properly configured HEC-token with the indexes that you want to send data to assigned.
- A Splunk Enterprise connection, if using the Write to Splunk Enterprise function.
Steps
- After doing any transformations on your data, use the Filter streaming function to filter your events based on what index you want to send your events to.
- Branch your pipeline by clicking the + icon on the function node and add another filter function.
For example, if you want to send events with sourcetypecisco:asato one index and events with sourcetypesyslogto a different index, use a filter function witheq(get("sourcetype"),"cisco:asa");and another witheq(get("sourcetype"), "syslog");. - Add the Batch Events function to both of your branches with the following options filled out.
Field Description Example Num Events The maximum number of events to send per batch. Capped at 1000 events. 99; Millis The interval, in milliseconds, at which to send batched events. 1000; - End both of your branches with the Write to Index or Write to Splunk Enterprise sink functions.
a. If you are using the Write to Index function, fill out the following fields.Field Example module literal(""); dataset literal("index_name");
b. If you are using the Write to Splunk Enterprise function, select a connection from the drop-down menu and fill out the following fields.Field Example index literal("index_name"); Parameters async = true If your index is set in your data's attributes, you can type
cast(map-get(get("attributes"), "index"), "string");to send your data to the index specified in your data. - Save and activate your pipeline.
| Formatting metrics data | Performance expectations for sending data from a data pipeline to Splunk Enterprise |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Data Stream Processor: 1.0.0
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!