SPL to SPL2 conversion tool
The SPL to SPL2 conversion tool assists you in converting SPL to SPL2 in specific Splunk products.
How the conversion tool works
In a user interface (UI) that supports SPL2, you can use snippets of SPL in your searches and pipelines by enclosing the snippets in backtick ( ` ) characters. These snippets of SPL are referred to as search literals and are described in the SPL2 Search Manual.
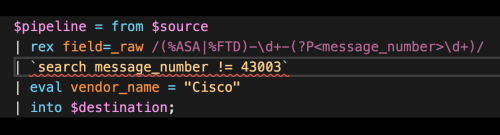
When you specify SPL in a UI that supports SPL2, a visual indicator appears under the SPL portion of the search. The visual indicator is a squiggly line, as shown in the following image.
- If the SPL can be converted to SPL2, the squiggly line is yellow.
- If there are multiple issues, if some of the SPL can't be converted to SPL2, or if there is an error in the SPL2, the squiggly line is red.
The conversion tool proposes commands and other search language suggestions. You can either accept the conversion suggestions, or type the SPL2 yourself to convert the SPL to SPL2.
The converter does not convert every piece of SPL to SPL2, but makes a best effort to convert what it can.
Adjust for the implied search command
SPL2 does not recognize the implied search command that occurs in SPL searches. Consider the following search snippet:
status_code IN (40*, 50*))
This snippet, while valid in SPL when placed at the beginning of a search, is invalid in SPL2.
SPL2 expects a command before this snippet, for example:
search status_code IN (40*, 50*))
Sample conversion messages
When SPL can be converted to SPL2, the conversion tool displays messages similar to the following:
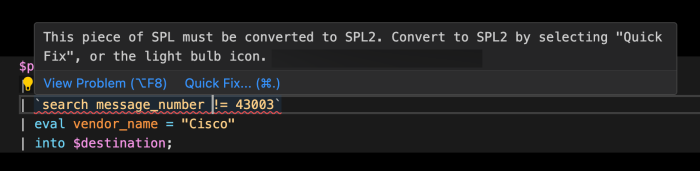
This piece of SPL must be converted to SPL2. Convert to SPL2 by selecting "Quick Fix", or the light bulb icon.
Convert the 'search' clause to the 'where' clause by selecting "Quick Fix", or the light bulb icon.
If you position your cursor over the syntax with the visual indicator, a brief explanation of the syntax issue appears along with options to view or fix the issue.
In pipelines, if you don't use backtick ( ` ) characters the error message you see will not have the option to convert the SPL snippets to SPL2.
Steps to convert SPL syntax
To convert the SPL syntax to SPL2:
- Ensure the SPL is enclosed in backtick ( ` ) characters.
- Choose one of the following methods to convert the syntax:
- Hover your cursor over the squiggly line.
- Position your cursor anywhere in the underlined snippet an press F8.
A description of the syntax issue appears along with the Quick Fix icon.
In the following image, the Quick Fix recommendation is to
Convert the 'search' clause to the 'where' clause by selecting "Quick Fix", or the light bulb icon. - Select Quick Fix to convert the syntax.
Common conversion scenarios
The following table describes how various conversion issues are handled:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| search command | The search command is not supported in pipelines. The conversion tool attempts to map SPL search command syntax to the SPL2 where command syntax.
For example this pipeline uses the $pipeline = from $source | rex field=_raw /(%ASA|%FTD)-\d+-(?P<message_number>\d+)/ | search message_number != 43003 | eval vendor_name = "Cisco" | into $destination; The search command is converted to the where command: $pipeline = from $source | rex field=_raw /(%ASA|%FTD)-\d+-(?P<message_number>\d+)/ | where message_number != 43003 | eval vendor_name = "Cisco" | into $destination; The |
| search command and literal terms | Search clauses that contain literal terms without wildcards, such as search 404, are not supported with the SPL2 profiles for edgeProcessor and ingestProcessor because the search command is not supported for those profiles.
For example: search 404 Change this search literal using the where like(<field>, 404) Search clauses with literal terms are supported in the SPL2 profile for splunkd. |
| search command and filtering by an index | In pipelines, search clauses that use an index to filter data is not supported. Pipelines are processing pre-indexed data.
For example, this pipeline is not supported: $pipeline = from $source | search index=threats | into $destination |
| search command and wildcard characters | SPL search literals that contain a wildcard character are not supported with the SPL2 profiles for edgeProcessor and ingestProcessor.
search error* You must manually rewrite the search clause using the In most cases SPL search clauses that contain a wildcard character in a field-value pair can be converted to SPL2. The conversion uses the For example: search sourcetype=*.csv Converts to: where like(sourcetype, "%.csv") SPL search clauses that contain both the wildcard character ( * ) and the percent symbol ( % ) are not supported with the SPL2 profiles for edgeProcessor and ingestProcessor.
For example, the following search clause can't be converted: search host=my%host* You must use the |
| TERM and CASE search directives | The CASE search directive converts to the where command, because both the directive and command expect case-sensitivity.
The TERM search directive is supported in the SPL2 profile for splunkd. |
| Unsupported commands | Some SPL commands are not supported in SPL2. In some cases the conversion tool can substitute another command for the unsupported command.
$pipeline = | from $source |rex field=_raw /(%ASA|%FTD)-\d+-(?P<message_number>\d+)/ | search 'message-number' != 43003 | eval vendor_name = "Cisco" | fields - message-number | stats count | into $destination; The $pipeline = | from $source |rex field=_raw /(%ASA|%FTD)-\d+-(?P<message_number>\d+)/ | where 'message-number' != 43003 | eval vendor_name = "Cisco" | fields - message-number | stats count | into $destination; |
| from command | The from command in SPL and SPL2 are very different. The conversion tool maps the SPL from command to the SPL2 from command syntax.
|
| Regular expressions in commands and functions | The conversion tool determines if the correct regular expression syntax, PCRE or RE2, is used in the supported profile. |
| NOT LIKE | Support added to SPL2 for the NOT logical operator in combination with the LIKE eval function. |
| Escaping characters | Better support for the following escaping characters:
|
| Concatenation | In SPL, the concatenation operator is the period ( . ) character. However, in SPL2 the concatenation operator is the plus ( + ) symbol.
|
| Time modifiers | The time modifiers, such as earliest, latest, starttime, and endtime, are not supported in the SPL2 profiles for edgeProcessor and ingestProcessor. If a time modifier is detected, no conversion takes place and the pipeline remains unchanged.
|
| IN operator | Search clauses that use the IN operator are converted to the where command and the in eval function.
search status_code IN (400, 401, 402)) Converts to this: where upper(status_code) IN (upper("400"), upper("401"), upper("402")))For example, this SPL search clause includes wildcard characters: search status_code IN (40*, 50*)) Converts to the where like(status_code, "40%") OR like(status_code, "50%")) |
| spl1 command | The spl1 command, which is a new SPL2 command, is not supported in the SPL2 profiles for edgeProcessor and ingestProcessor.
|
See also
- Related information
- SPL2 compatibility profiles
- Differences between SPL and SPL2
- Understanding SPL2 syntax
| Differences between SPL and SPL2 | New features in SPL2 |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Cloud Services: current
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!