Add intelligence to improve data quality using Splunk Intelligence Management
The data management layer of Splunk intelligence Management helps you to combine your internal data with internal and external intelligence sources and provide automated threat intelligence. This helps to improve the quality of information that you exchange between Splunk Intelligence Management and your security tools.
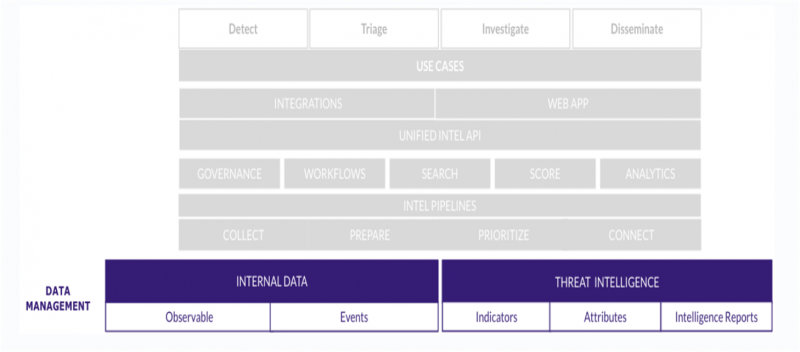
The following figure indicates the various components of the data management layer within the multilayered architecture of Splunk Intelligence Management:
What is internal data?
Internal data is the raw data generated within your organization, such as logs, emails, and network traffic. When you submit the raw data to Splunk Intelligence Management, it gets enriched and shared internally and externally to assist in security investigations and detections. Data submitted to Splunk Intelligence Management starts out as an event. Each event can contain observables.
What is threat intelligence?
Threat Intelligence provides an outside opinion or context to observables, such as maliciousness or attributes. Threat intelligence can include actors, campaigns, malware, Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs), and other objects. You can combine external intelligence sources with your internal historical data to label and score internal events or suspicious alerts, which automates the process of investigation and accelerates your response to events.
Maximize the threat intelligence coverage, which is the surface area to which these intelligence sources add labels to unlabeled data in the form of scores or context. You can maximize coverage by choosing the best sources for your organization despite budget constraints.
Splunk Intelligence Management categorizes threat Intelligence into the following types:
- Premium intelligence sources: Privately maintained sources that require some commercial relationship with the provider or membership in a group, such as an ISAC or ISAO. The providers of these sources are intelligence specialists who curate and disseminate valuable enriched intelligence.
- Open Sources: Public data that is available to everyone, including blogs, RSS feeds, and open APIs. These sources are less curated and provide less valuable labels such as scores.
- Internal Intelligence: The organization's curated historical data from incidents and investigations. Internal intelligence can include internally generated reports, closed cases, tickets, phishing emails, and associated tags. Internal intelligence is the most valuable intelligence resource for your security workflow as compared to external sources because they contain the most relevant and approved context. Internal intelligence helps to evaluate observables and events in raw data sources such as logs and network traffic and help to decide how to prioritize such events in the future.
To learn more about the commonly used terminology in Splunk Intelligence Management, see
Glossary.
See also
| Automate security operations using Splunk Intelligence Management | Normalize data from multiple sources using Splunk Intelligence Management |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Intelligence Management (Legacy): current
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!