Part 2: Monitor your Kubernetes cluster 🔗
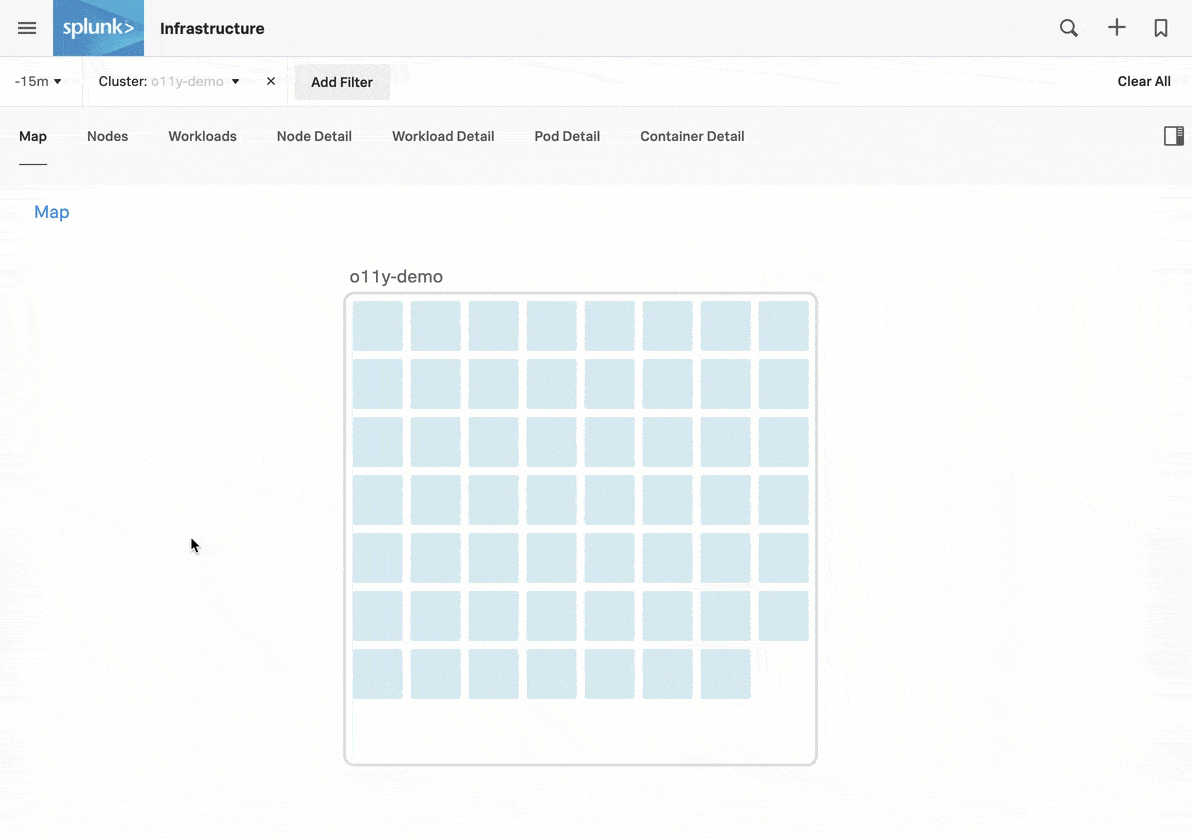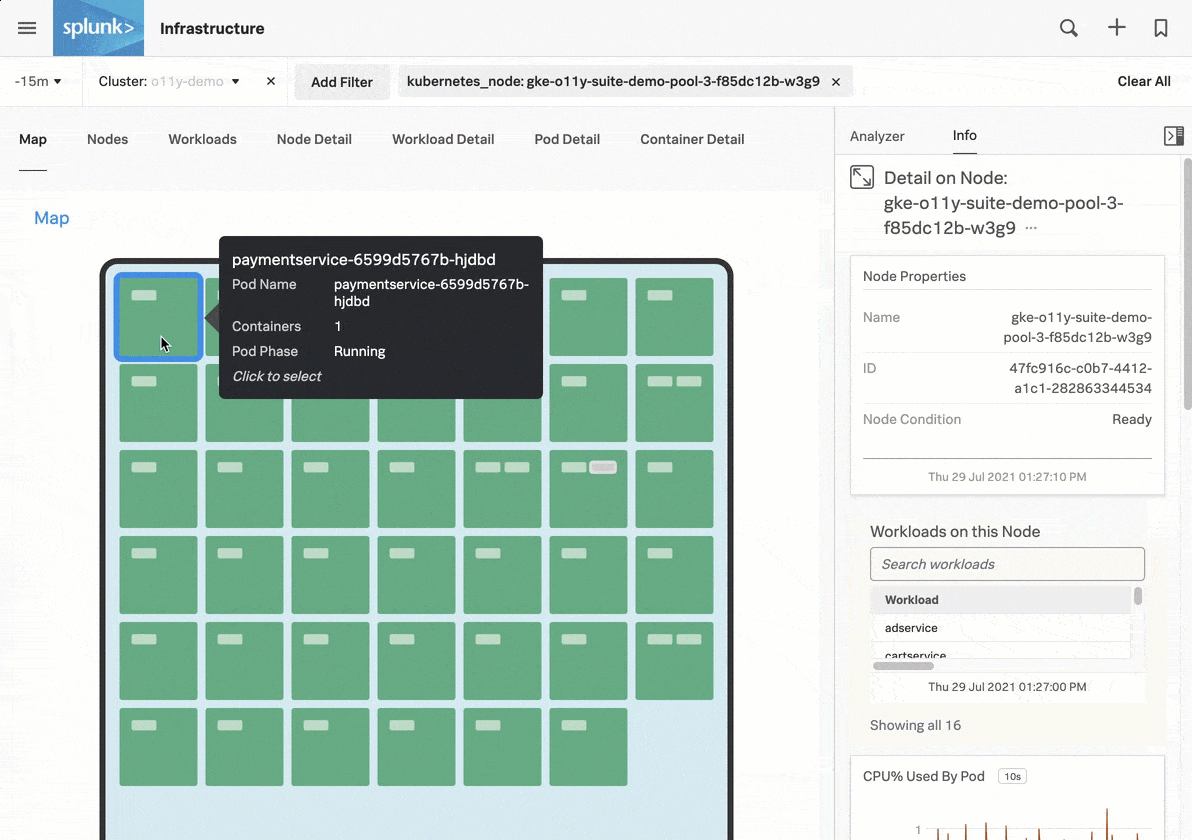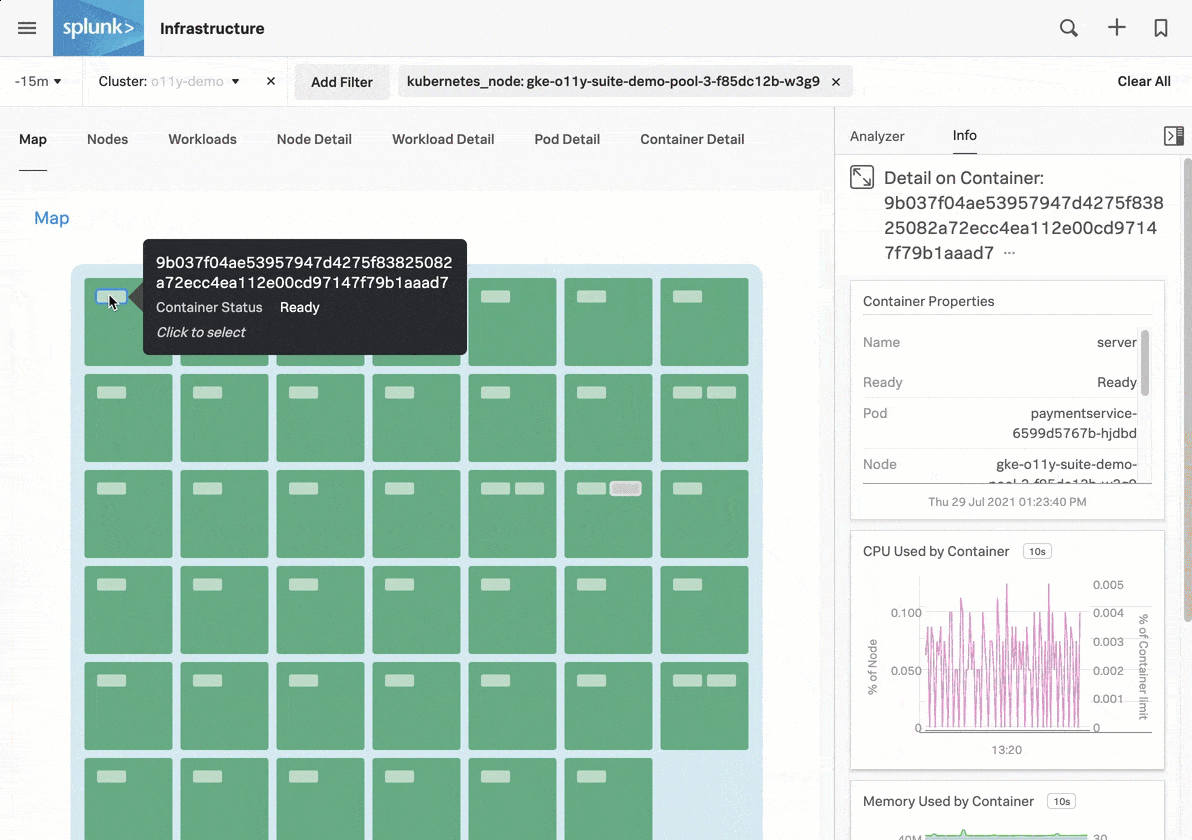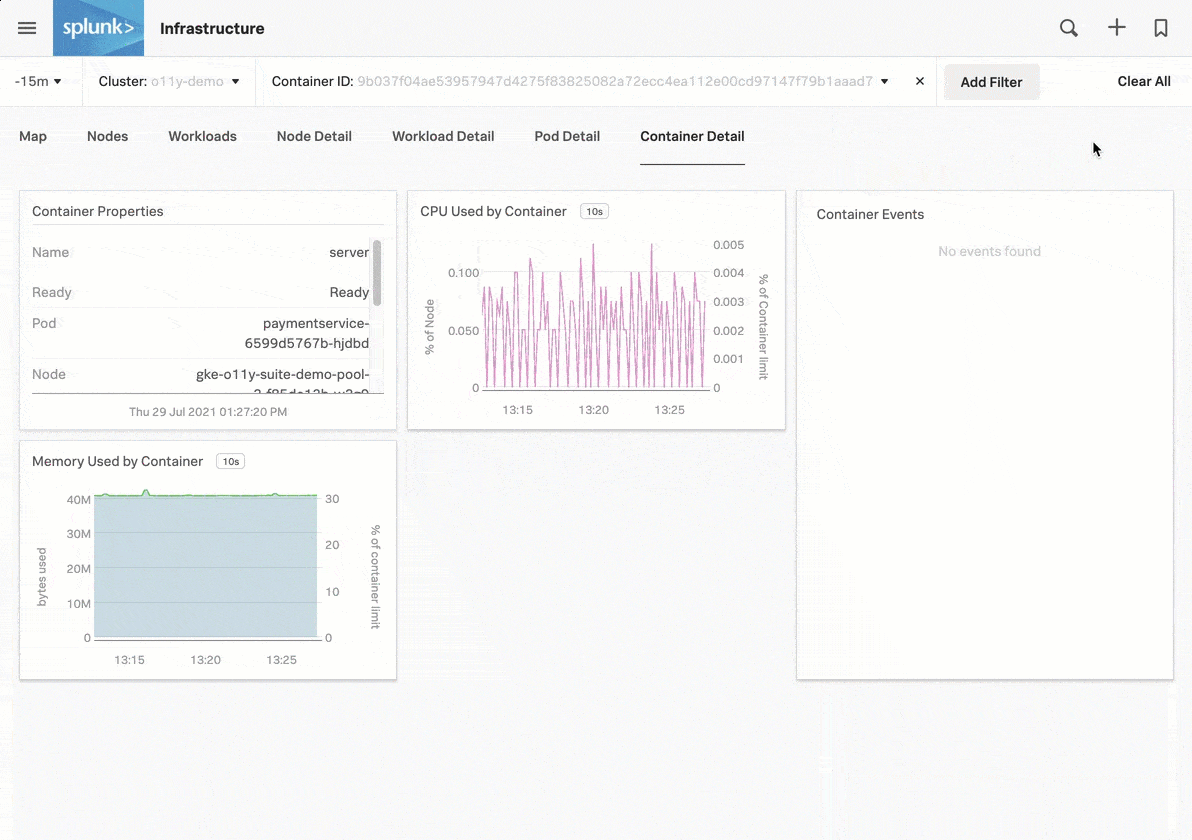
Now that you have Kubernetes cluster data flowing into Splunk Observability Cloud, you can use built-in navigators to explore your data. For an overview of the tutorial, see Tutorial: Monitor your Kubernetes environment in Splunk Observability Cloud.
Note
Navigators appear only if Splunk Infrastructure Monitoring is receiving data from your source.
For example, even if the guided setup that you used in Part 1: Install the Collector and get Kubernetes data into Splunk Observability Cloud provided confirmation of a valid connection, the navigators don’t display unless your host, Kubernetes cluster, or cloud provider service is actively sending data to Splunk Infrastructure Monitoring.
If you don’t see a navigator after 15 minutes of making a valid connection, check your source to verify that it is generating data. For example, verify that your host, cluster, or service generates data that it can send to Splunk Infrastructure Monitoring.
Explore Kubernetes data using built-in dashboards 🔗
Splunk Observability Cloud also provides built-in dashboards that you can use to explore your Kubernetes data. To see which built-in dashboards are available, refer to Dashboards in Splunk Observability Cloud.
To access the built-in dashboards, follow these steps:
Open the navigation Menu and select Dashboards. The Dashboards page displays.
Search for Kubernetes. The Kubernetes dashboard group displays.
Select a link to access a relevant dashboard.
Next step 🔗
This completes the second part of the tutorial. You’ve learned how to use built-in navigators to explore your data.
Next, learn how to create a built-in detector to alert you about your Kubernetes data. To continue, see Part 3: Activate a built-in detector to issue alerts.
Learn more 🔗
For more details about using navigators in general, see Use navigators in Splunk Infrastructure Monitoring.
For more details about the data displayed in the Kubernetes navigator, see Use the Kubernetes navigator.
For more details about working with charts, see Charts in Splunk Observability Cloud.