Instrumentation-specific data for Browser RUM 🔗
Splunk RUM for Browser collects the following data through instrumentation. To activate or deactivate instrumentations, see Instrumentation settings.
Document load 🔗
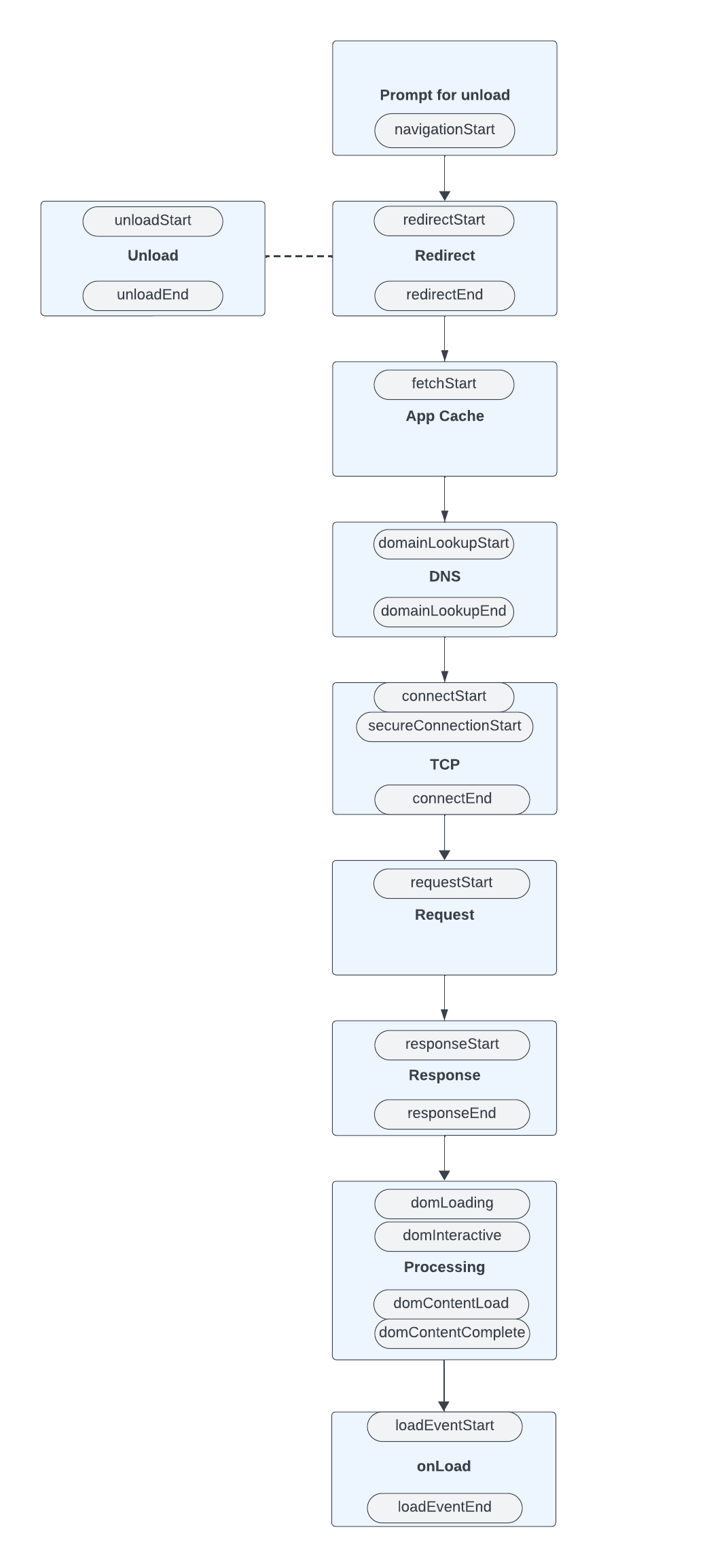
The document instrumentation produces spans about resources that load by the time the Window:load event fires. The root span generated is documentLoad. “The parentID for the documentFetch and resourceFetch spans is documentLoad.id.
If the page load request has a Server-Timing header, RUM uses the data to link the documentFetch span to the corresponding back-end span. The Browser RUM agent also collects resources such as script, link, css - font, iframe, XHR/fetch, img, favicon and manifest.json, and links them to APM traces if the Server-Timing header is present.
documentLoad 🔗
The Browser RUM agent collects the following data using the documentLoad instrumentation:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
String |
URI of the referral page. For example, |
|
String |
Width and height of the display. For example, |
The following annotations are collected from the navigation timings, as specified by the W3C specification for the PerformanceNavigationTiming interface:
Name |
Timestamp |
|---|---|
|
Immediately before the browser starts fetching the resource. |
|
Immediately before the user agent starts the unload event of the previous document. |
|
Immediately after the user agent finishes the unload event of the previous document. |
|
Immediately before the user agent sets the readiness of the current document to Interactive. |
|
Immediately before the user agent fires the |
|
Immediately after the |
|
Immediately before the browser sets the readiness of the current document to Complete. |
|
Immediately before the load event of the current document is fired. |
|
When the load event of the current document is completed. |
This diagram shows the sequence of events in documentLoad.
documentFetch 🔗
The Browser RUM agent collects the following data using the documentFetch instrumentation:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Number |
The size of the document received from the payload body. |
|
String |
Trace identifier, collected from the |
|
String |
Span identifier, collected from the |
resourceFetch 🔗
The Browser RUM agent collects the following data using the resourceFetch instrumentation:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Number |
The size of the document received from the payload body. |
|
String |
URL of the requested resource. |
|
String |
Trace identifier, collected from |
|
String |
Span identifier, collected from |
Note
Safari 10.1 doesn’t support resourceFetch spans.
XHR and Fetch instrumentations 🔗
The xhr and fetch instrumentations collect XMLHttpRequest events and Fetch API events. Spans differ in the value of the component tag, which differentiates between xml-http-request and fetch.
This instrumentation prepends the HTTP method name to the name of the span. If the instrumentation maps to a back end
providing a Server-Timing header in the response, the link with the back-end trace is also generated.
The Browser RUM agent collects the following data using the XHR and Fetch instrumentations:
http.methodhttp.response_content_lengthhttp.hosthttp.schemehttp.status_codehttp.status_texthttp.user_agenthttp.url
The XHR and Fetch instrumentations annotate the span with timestamps representing when the following events fire:
Event |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Number |
Time in UNIX epoch, measured in microseconds when the XHR |
|
Number |
Time when the XHR |
|
Number |
Time when the XHR |
|
Number |
Time when the XHR |
|
Number |
Time when the XHR |
|
Number |
Time when the XHR |
Annotations collected by the XHR and Fetch instrumentations are described in Request timing annotations.
Web Vitals 🔗
The webvitals instrumentation collects data about Google Web Vitals metrics. The Browser RUM agent collects Web Vitals metrics as spans with zero duration. Every span has a designated traceId and no parent span.
The Browser RUM agent collects the following data using the webvitals instrumentation:
Name |
Web Vital |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Largest Contentful Paint |
Measures loading performance by capturing the render time of the largest image or text block visible within the viewport. |
|
First Input Delay |
Measures interactivity by capturing the timestamp between user interactions to time when the browser can begin processing event handlers in response to that interaction. |
|
Cumulative Layout Shift |
Measures visual stability by capturing the sum of all individual layout shift scores for every unexpected layout shift that occurs during the entire lifespan of the page. A layout shift occurs any time a visible element changes its position from one rendered frame to the next. |
|
Interaction to Next Paint |
Measures responsiveness by observing the latency of all interactions a user has done on the page and reports the slowest value. |
Resources after load 🔗
The postload instrumentation collects data about resources that load after a page load event. By default, the instrumentation activates instrumenting <script> and <img> resources. Typically, you might use the postload instrumentation to collect telemetry when loading images on scroll events.
Spans collected by the postload instrumentation match the data model described in resourceFetch.
User interactions 🔗
The interactions instrumentation collects telemetry data on interactions on elements that have a registered event listener of the type Element.addEventListener. Events collected by the listener generate a span with a name matching the DOM event name.
The Browser RUM agent collects the following data using the interactions instrumentation:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
String |
Name of the event. For example, |
|
String |
Name of the target element. For example, |
|
String |
XPath of the target element. |
Visibility 🔗
The visibility instrumentation collects visibilitychange events. Visibility changes that happen when a page refreshes aren’t recorded, as the browser tab might never go visible.
The Browser RUM agent collects the following data using the visibility instrumentation:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Boolean |
Whether the page is hidden or not. |
Connectivity 🔗
The connectivity instrumentation collects offline and online events. The browser records offline events when the browser goes offline and is cached in memory until the browser goes online. Offline and online events are sent at the same time.
The Browser RUM agent collects the following data using the connectivity instrumentation:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Boolean |
Whether the browser went online or offline. |
History API 🔗
The Browser RUM agent also instruments the History API to provide visibility into the session history of the browser. The History API tracks URL changes that don’t reload the page and is used in single-page applications.
The instrumentation also tracks URL changes that occur by changing the location.hash by listening to hashchange events. Route changes have no duration. The routeChange span contains the following tags:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
String |
The value is always |
|
String |
Page URL prior to the route change. |
|
String |
Page URL after the route change. |
Long tasks 🔗
The longtask instrumentation collects information about long tasks. The Browser RUM agent creates a span for every long task detected.
Span attributes include the containers where that task occurred. For tasks that don’t occur within the top level page, the containerId, containerName, and containerSrc fields provide information about the source of the task.
The Browser RUM agent collects the following data using the longtask instrumentation:
Name |
Type |
|---|---|
|
String |
|
Number |
|
Number |
|
String |
|
String |
|
Number |
|
Number |
|
String |
|
String |
|
String |
|
String |
Websockets 🔗
The websockets instrumentation collects websocket lifecycle events and uses it to populate spans. The instrumentation collects spans from websocket connect, send, and onmessage events.
connect 🔗
The websockets instrumentation collects the following data from connect events:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
String |
The Websocket URL. |
|
Number |
Time lapsed between a websocket constructor call and the |
|
String or array |
Protocols passed to the websocket constructor. |
|
String |
The value can be |
|
String |
Websocket error event message. |
send and onmessage 🔗
The websockets instrumentation collects the following data from send and onmessage events:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
String |
The Websocket URL. |
|
Number |
Payload size in bytes. |
Socket.io messages 🔗
The Socket.io instrumentation generates spans from messages sent using the socket.io client library. Spans conform to the OpenTelemetry specifications on messaging systems. This instrumentation is deactivated by default.
When using the standalone socket.io build, activate the instrumentation by passing true to the configuration setting, as in the following snippet:
<script src="/location/to/splunk-otel-web.js"></script>
<script>
SplunkRum.init({
// ...
instrumentations: {
socketio: true
}
});
</script>
<script src="/socket.io/socket.io.js"></script>
When using both the @splunk/otel-web and the socket.io-client npm packages in the same bundle, pass the socket.io client to the instrumentation using the target setting:
import SplunkOtelWeb from '@splunk/otel-web';
import { io } from 'socket.io-client';
SplunkRum.init({
// ...
instrumentations: {
socketio: {
target: io,
},
},
});
When using the CDN distribution of Splunk RUM, activate the socket.io instrumentation and expose the io function as window.io, as in the following example:
<script src="/location/to/splunk-otel-web.js"></script>
<script>
SplunkRum.init({
// ...
instrumentations: {
socketio: true
}
});
</script>
<script src="/app.min.js"></script>
The content of the app.min.js file in the previous example is the following:
import { io } from 'socket.io-client';
window.io = io;
const socket = io();
// ...
You can use a different global variable name by specifying it as the target:
SplunkRum.init({
// ...
instrumentations: {
socketio: {
target: 'socketIoClient',
},
},
});
// Expose the io object in your bundle
window.socketIoClient = io;
Messages sent between socket.io clients and servers produce EVENT_NAME send spans when the messages go from client to server, and EVENT_NAME receive spans when the messages go from server to client. Both types of spans contain the following attributes:
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
String |
The value is always |
|
String |
The value of the socket.io namespace. |
|
String |
The value is always |
|
String |
Name of the event, the first argument of the |