Plan your deployment
The Splunk App for Enterprise Security operates on large volumes of data from many different sources. Before you install the Splunk App for Enterprise Security in a production environment, plan your architecture based on your Splunk deployment. You can install Splunk App for Enterprise Security on a single server, but if you are capturing and reporting on a large volume of data, you get the best results from a distributed deployment of Splunk for Enterprise Security. This section helps you to determine the appropriate deployment architecture for your environment and needs.
Prepare for installation
Make sure you have all the information you need and the appropriate access to the servers in your Splunk deployment before you install the Splunk App for Enterprise Security. The following table lists the information you need to set up the Splunk App for Enterprise Security.
| Component | Required Information | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Search head | "sudo" or "administrator" console login access required to this server. | Need Splunk admin user name and password. |
| Deployment server (optional) | Name of each deployment client and the relevant server classes. | Configure the deployment clients on the server to define which applications must be installed on the client. |
| Indexers | URL and Splunk port, and Splunk admin account and password. | |
| Forwarders | Deployment server URL and port | |
| Data inputs For each data input you need to know: |
* the associated add-on. | |
| * Any required configuration changes to the add-on. | See the README for the add-on.
| |
| * Correct source type | Automatically discovered in some cases. See the README for the add-on.
| |
| * Data source or location | ||
| * Splunk input type | UDP, TCP, scripted input, etc. | |
| * Data destination | forwarder or indexer | |
| Assets and Identities | See Identity Manager for information that must be contained in the asset list. See "Supporting dashboards" in the Splunk App for Enterprise Security User Manual for information about identities. |
Common deployment architectures
This topic covers how to install the Splunk App for Enterprise Security in the following existing deployment architectures:
- Single-server deployment
- Distributed multiserver deployment
Splunk recommends that the Splunk App for Enterprise Security be installed on its own search head or search head pool. This increases the resource availability and eliminates possible conflicts with other apps installed on the same Splunk deployment.
Splunk component types
The following table shows which Splunk App for Enterprise Security files need to be installed on each component of a distributed deployment.
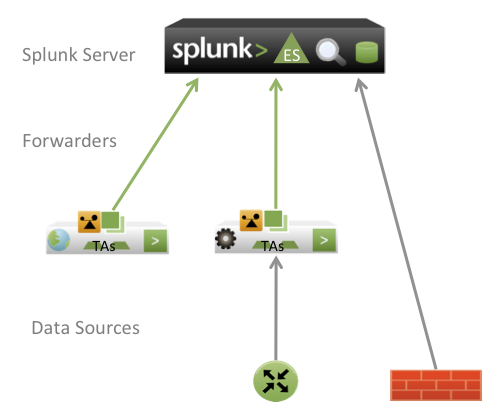
Single server deployments
For simple deployments, you can use a single server with Splunk for Enterprise Security installed. This configuration, primarily used for a lab or test environment, can support one or two users running concurrent searches. See the "Hardware capacity planning for your Splunk deployment" in the Splunk documentation for limitations for a single-server deployment.
To get data from remote servers and applications logging locally to those systems, Splunk recommends that you use Splunk forwarders, lightweight instances of Splunk that that gather data and send it to indexers in real time. To manage the forwarders from a centralized location, configure the Splunk deployment server on the main search head/indexer.
Distributed multiserver deployments
For Splunk for Enterprise Security, a three-tier Splunk deployment is recommended, where search is separated from indexing. This allows for more efficient use of hardware, and lets search usage scale more or less independently of index volume. Multiple indexers allow Splunk to distribute the workload of processing incoming events and improve search performance by splitting the search overhead between multiple servers, systems, and applications. The main Splunk documentation provides a section called "Dimensions of a Splunk deployment", describing the amount of indexing and searching that make a distributed deployment necessary.
Note: Although it is possible to deploy Splunk using multiple indexers as search peers, a dedicated search head is recommended as soon as the Splunk for Enterprise Security moves to a multiserver deployment. The dashboards and alerts in Splunk for Enterprise Security rely on a large number of scheduled searches, which can place a search load on the systems even when users are not running manual searches.
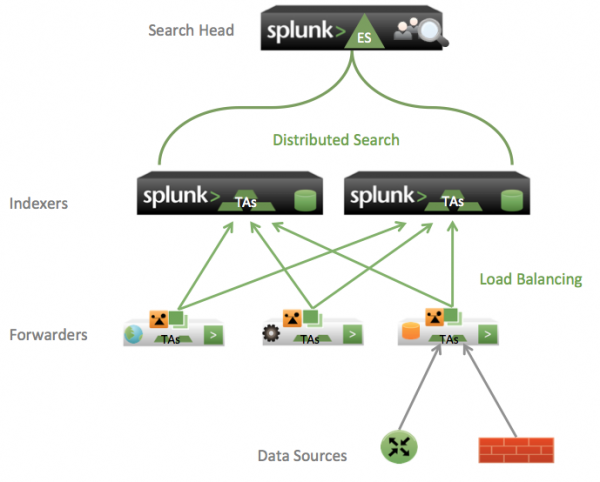
This diagram shows a typical distributed deployment:
Note: In very large deployments, multiple tiers of forwarders may be advisable.
The recommended deployment has the following components:
- Search head: A Splunk instance that directs search requests to one or more search peers. The search head needs to have the full Splunk for Enterprise Security application installed. For larger deployments, you might want to deploy multiple search heads.
- Indexer: A Splunk instance that indexes data, transforming raw data into events and placing the results into an index. Indexers should not have a complete installation of Splunk for Enterprise Security; install only add-ons you need for the data inputs. Indexers sometimes perform other key Splunk functions: data input and searches. In larger deployments, forwarders handle the input of data, which they send on to the indexer for indexing.
- Forwarders: Distributed Splunk instances that obtain and forward data to the indexers. Forwarders allow load balancing between indexers. Forwarders can monitor a local file system, use scripted inputs to gather data, or accept data over UDP or TCP. Full or heavy forwarders can assign source types and ensure that data coming into the indexers is identified correctly. Install add-ons for specific data on the full forwarder.
Note: Add-ons containing knowledge needed for search time knowledge mapping of data need to be installed on the full forwarders.
Using the Splunk App for Enterprise Security with other apps
The Splunk App for Enterprise Security relies heavily on the knowledge supplied in the add-ons. These add-ons specify the complex processing necessary to optimize, normalize, and categorize your IT security data for use in Enterprise Security. Apps and add-ons that have been developed separately from Enterprise Security might include data knowledge that has not been normalized for Enterprise Security and might overwrite fields that Enterprise Security extracts, preventing the proper functioning of the Enterprise Security searches and dashboards that rely on those fields.
Note: For optimal performance of the Splunk App for Enterprise Security, Splunk recommends that it be installed on a dedicated search head without other apps installed and that indexers use only the necessary Enterprise Security compatible add-ons.
In some cases, it might be necessary to install other apps on the same search head or server as the Splunk App for Enterprise Security. Many apps and add-ons provided by Splunk are compatible with Enterprise Security. Compatible apps are documented as such on the Splunk Apps download page for the app. Installing apps or add-ons that are not designated as compatible with Enterprise Security can have a negative impact on the performance of the the Splunk App for Enterprise Security and prevent data from being processed correctly (thus, preventing some data from appearing on dashboards).
| Solution architecture | Prerequisites |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise Security: 3.0, 3.0.1

 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!